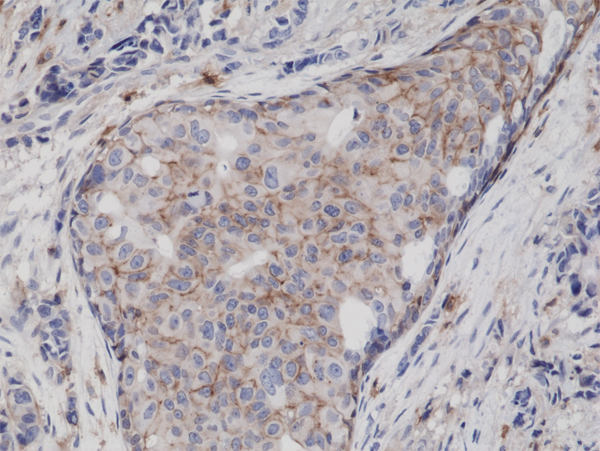
CD44 Antibody (Rabbit Monoclonal)
Clone RM264
The CD44 Antibody (Rabbit Monoclonal, Clone RM264) is a high-affinity, precision-engineered antibody developed for the specific detection of CD44, a transmembrane glycoprotein involved in cell-cell interactions, cell adhesion, migration, and tumor progression. CD44 is expressed on a wide range of cell types, including lymphocytes, monocytes, epithelial cells, and various cancer stem cells, making it a critical biomarker for studying cancer biology, immune responses, and stem cell research.
Clone RM264 is a rabbit monoclonal antibody optimized for immunohistochemistry (IHC) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues, as well as flow cytometry and immunofluorescence (IF) applications. It provides robust and consistent membranous staining of CD44-positive cells in normal and pathological tissues. This includes lymphoid organs and solid tumors such as breast, colorectal, prostate, and gastric carcinomas, where CD44 expression correlates with tumor aggressiveness, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance.
RM264 is widely used in oncology research, tumor microenvironment studies, and diagnostic pathology to evaluate tumor heterogeneity and cancer stem cell populations. Its high specificity and minimal background ensure accurate and reproducible results, supporting both research and clinical diagnostics.
Key Features:
Clone: RM264
Host Species: Rabbit Monoclonal
Target Antigen: CD44 (Cell surface glycoprotein involved in cell adhesion)
Applications:
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Flow Cytometry
Immunofluorescence (IF)
Sample Types: FFPE tissues, tumor biopsies, lymphoid tissue, blood
Localization: Cell surface membrane
Species Reactivity: Human (others upon validation)
Research Areas:
Cancer biology and tumor progression
Cancer stem cell research
Immune system and inflammation studies
Tumor microenvironment analysis
Prognostic marker evaluation in solid tumors
The CD44 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody, Clone RM264, is a highly reliable reagent for detecting CD44 expression in both normal and malignant tissues. Its excellent sensitivity and specificity make it an essential tool for cancer diagnostics, therapeutic targeting, and immune profiling in translational research and pathology labs.