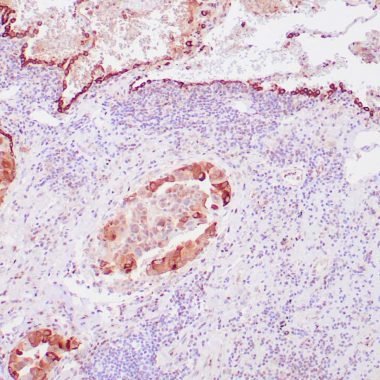
Product Overview
GM124/Monospecific Mouse/Monoclonal
GeneBio’s recombinant mouse antibody recognizes Surfactant. Pulmonary Surfactant is primarily responsible for lowering the surface tension at the air-liquid interface in the alveoli, a process that is essential for normal respiration. Pulmonary Surfactant is a mixture of phospholipids and proteins, including four distinct surfactant-associated proteins (SPs), SP-A, SP-B, SP-C, SP-D. SP-B and SP-C are predominantly hydrophobic proteins that associate with lipids to promote the absorption of surfactant phospholipids and to reduce the surface tension in the alveoli. SP-A and SP-D are large multimeric proteins belonging to the family of calcium-dependent lectins, designated Collectins, which contribute to the innate immune system. Both SP-A and SP-D have been shown to protect against microbial challenge through binding to the lipid components of the bacterial cell wall and facilitating the rapid removal of microbials.
Surfactant proteins in different glandular structures of the oral cavity display antimicrobial activity for protection of invading microorganisms. Moreover, they are involved in lowering liquid tension in fluids and facilitate secretion flows.